배열(array)은 1개의 변수에 여러 개의 값을 순차적으로 저장할 때 사용한다. 자바스크립트의 배열은 객체이며 유용한 내장 메소드를 포함하고 있다.
배열은 Array 생성자로 생성된 Array 타입의 객체이며 프로토타입 객체는 Array.prototype이다.
1. 배열의 생성
1.1 배열 리터럴
0개 이상의 값을 쉼표로 구분하여 대괄호([])로 묶는다. 첫번째 값은 인덱스 ‘0’으로 읽을 수 있다. 존재하지 않는 요소에 접근하면 undefined를 반환한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
const emptyArr = [];
console.log(emptyArr[1]); // undefined
console.log(emptyArr.length); // 0
const arr = [
'zero', 'one', 'two', 'three', 'four',
'five', 'six', 'seven', 'eight', 'nine'
];
console.log(arr[1]); // 'one'
console.log(arr.length); // 10
console.log(typeof arr); // object
위의 배열을 객체 리터럴로 유사하게 표현하면 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
const obj = {
'0': 'zero', '1': 'one', '2': 'two',
'3': 'three', '4': 'four', '5': 'five',
'6': 'six', '7': 'seven', '8': 'eight',
'9': 'nine'
};
배열 리터럴은 객체 리터럴과 달리 프로퍼티명이 없고 각 요소의 값만이 존재한다. 객체는 프로퍼티 값에 접근하기 위해 대괄호 표기법 또는 마침표 표기법을 사용하며 프로퍼티명을 키로 사용한다. 배열은 요소에 접근하기 위해 대괄호 표기법만을 사용하며 대괄호 내에 접근하고자 하는 요소의 인덱스를 넣어준다. 인덱스는 0부터 시작한다.
두 객체의 근본적 차이는 배열 리터럴 arr의 프로토타입 객체는 Array.prototype이지만 객체 리터럴 obj의 프로토타입 객체는 Object.prototype이라는 것이다.
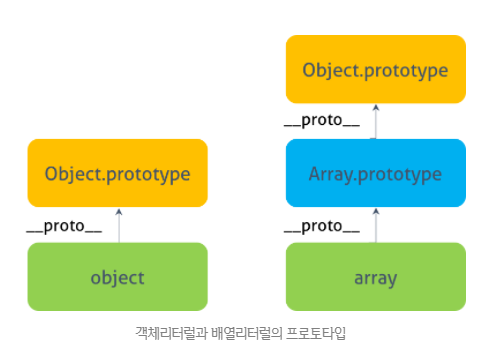
1
2
3
4
5
const emptyArr = [];
const emptyObj = {};
console.dir(emptyArr.__proto__);
console.dir(emptyObj.__proto__);

대부분의 프로그래밍 언어에서 배열의 요소들은 모두 같은 데이터 타입이어야 하지만, 자바스크립트 배열은 어떤 데이터 타입의 조합이라도 포함할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
const misc = [
'string',
10,
true,
null,
undefined,
NaN,
Infinity,
['nested array'],
{ object: true },
function () {}
];
console.log(misc.length); // 10
1.2 Array() 생성자 함수
배열은 일반적으로 배열 리터럴 방식으로 생성하지만 배열 리터럴 방식도 결국 내장 함수 Array() 생성자 함수로 배열을 생성하는 것을 단순화시킨 것이다. Array() 생성자 함수는 Array.prototype.constructor 프로퍼티로 접근할 수 있다.
Array() 생성자 함수는 매개변수의 갯수에 따라 다르게 동작한다.
매개변수가 1개이고 숫자인 경우 매개변수로 전달된 숫자를 length 값으로 가지는 빈 배열을 생성한다.
1
2
const arr = new Array(2);
console.log(arr); // (2) [empty × 2]
그 외의 경우 매개변수로 전달된 값들을 요소로 가지는 배열을 생성한다.
1
2
const arr = new Array(1, 2, 3);
console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3]
2. 배열 요소의 추가와 삭제
2.1 배열 요소의 추가
객체가 동적으로 프로퍼티를 추가할 수 있는 것처럼 배열도 동적으로 요소를 추가할 수 있다. 이때 순서에 맞게 값을 할당할 필요는 없고 인덱스를 사용하여 필요한 위치에 값을 할당한다. 배열의 길이(length)는 마지막 인덱스를 기준으로 산정된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
const arr = [];
console.log(arr[0]); // undefined
arr[1] = 1;
arr[3] = 3;
console.log(arr); // (4) [empty, 1, empty, 3]
console.log(arr.lenth); // 4
값이 할당되지 않은 인덱스 위치의 요소는 생성되지 않는다는 것에 주의하자. 단, 존재하지 않는 요소를 참조하면 undefined가 반환된다.
1
2
3
4
5
// 값이 할당되지 않은 인덱스 위치의 요소는 생성되지 않는다.
console.log(Object.keys(arr)); // [ '1', '3' ]
// arr[0]이 undefined를 반환한 이유는 존재하지 않는 프로퍼티에 접근했을 때 undefined를 반환하는 것과 같은 이치다.
console.log(arr[0]); // undefined
2.2 배열 요소의 삭제
배열은 객체이기 때문에 배열의 요소를 삭제하기 위해 delete 연산자를 사용할 수 있다. 이때 length에는 변함이 없다. 해당 요소를 완전히 삭제하여 length에도 반영되게 하기 위해서는 Array.prototype.splice 메소드를 사용한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
const numbersArr = ['zero', 'one', 'two', 'three'];
// 요소의 값만 삭제된다
delete numbersArr[2]; // (4) ["zero", "one", empty, "three"]
console.log(numbersArr);
// 요소 값만이 아니라 요소를 완전히 삭제한다
// splice(시작 인덱스, 삭제할 요소수)
numbersArr.splice(2, 1); // (3) ["zero", "one", "three"]
console.log(numbersArr);
3. 배열의 순회
객체의 프로퍼티를 순회할 때 for…in 문을 사용한다. 배열 역시 객체이므로 for…in 문을 사용할 수 있다. 그러나 배열은 객체이기 때문에 프로퍼티를 가질 수 있다. for…in 문을 사용하면 배열 요소뿐만 아니라 불필요한 프로퍼티까지 출력될 수 있고 요소들의 순서를 보장하지 않으므로 배열을 순회하는데 적합하지 않다.
따라서 배열의 순회에는 forEach 메소드, for 문, for…of 문을 사용하는 것이 좋다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
const arr = [0, 1, 2, 3];
arr.foo = 10;
for (const key in arr) {
console.log('key: ' + key, 'value: ' + arr[key]);
}
// key: 0 value: 0
// key: 1 value: 1
// key: 2 value: 2
// key: 3 value: 3
// key: foo value: 10 => 불필요한 프로퍼티까지 출력
arr.forEach((item, index) => console.log(index, item));
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
console.log(i, arr[i]);
}
for (const item of arr) {
console.log(item);
}
4. Array Property
4.1 Array.length
length 프로퍼티는 요소의 개수(배열의 길이)를 나타낸다. 배열 인덱스는 32bit 양의 정수로 처리된다. 따라서 length 프로퍼티의 값은 양의 정수이며 2의 32승 - 1(4,294,967,296 - 1) 미만이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(arr.length); // 5
arr[4294967294] = 100;
console.log(arr.length); // 4294967295
console.log(arr); // (4294967295) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, empty × 4294967289, 100]
arr[4294967295] = 1000;
console.log(arr.length); // 4294967295
console.log(arr); // (4294967295) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, empty × 4294967289, 100, 4294967295: 1000]
주의할 것은 배열 요소의 개수와 length 프로퍼티의 값이 반드시 일치하지는 않는다는 것이다.
Note: 배열 요소의 개수와 length 프로퍼티의 값이 일치하지 않는 배열을
희소 배열(sparse array)이라 한다. 희소 배열은 배열의 요소가 연속적이지 않은 배열을 의미한다. 희소 배열이 아닌 일반 배열은 배열의 요소 개수와 length 프로퍼티의 값이 언제나 일치하지만 희소 배열은 배열의 요소 개수보다 length 프로퍼티의 값이 언제나 크다.희소 배열은 일반 배열보다 느리며 메모리를 낭비한다.
현재 length 프로퍼티 값보다 더 큰 인덱스로 요소를 추가하면 새로운 요소를 추가할 수 있도록 자동으로 length 프로퍼티의 값이 늘어난다. length 프로퍼티의 값은 가장 큰 인덱스에 1을 더한 것과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
const arr = [];
console.log(arr.length); // 0
arr[1000] = true;
console.log(arr); // (1001) [empty × 1000, true]
console.log(arr.length); // 1001
console.log(arr[0]); // undefined
Note: length 프로퍼티의 값은 명시적으로 변경할 수 있다. 만약 length 프로퍼티의 값을 현재보다 작게 변경하면 변경된 length 프로퍼티의 값보다 크거나 같은 인덱스에 해당하는 요소는 모두 삭제된다.
1
2
3
4
5
const arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ];
// 배열 길이의 명시적 변경
arr.length = 3;
console.log(arr); // (3) [1, 2, 3]
5. Array Method
- 메소드는 this(원본 배열)를 변경한다.
- 메소드는 this(원본 배열)를 변경하지 않는다.
Array 객체가 제공하는 유용한 고차 함수에 대해서는 배열 고차 함수에서 살펴보도록 하자.
- 5.1 Array.isArray(arg: any): boolean ES5
- 5.2 Array.from ES6
- 5.3 Array.of ES6
- 5.4 Array.prototype.indexOf(searchElement: T, fromIndex?: number): number ES5 (원본 배열 변경 X)
[5.5 Array.prototype.concat(…items: Array<T[] T>): T[] ES3 (원본 배열 변경 X)](https://poiemaweb.com/js-array#55-arrayprototypeconcatitems-arrayt–t-t–es3) - 5.6 Array.prototype.join(separator?: string): string ES1 (원본 배열 변경 X)
- 5.7 Array.prototype.push(…items: T[]): number ES3 (원본 배열 변경 O)
[5.8 Array.prototype.pop(): T undefined ES3 (원본 배열 변경 O)](https://poiemaweb.com/js-array#58-arrayprototypepop-t–undefined-%EF%B8%8F-es3) - 5.9 Array.prototype.reverse(): this ES1 (원본 배열 변경 O)
[5.10 Array.prototype.shift(): T undefined ES3 (원본 배열 변경 O)](https://poiemaweb.com/js-array#510-arrayprototypeshift-t–undefined-%EF%B8%8F-es3) - 5.11 Array.prototype.slice(start=0, end=this.length): T[] ES3 (원본 배열 변경 X)
- 5.12 Array.prototype.splice(start: number, deleteCount=this.length-start, …items: T[]): T[] ES3 (원본 배열 변경 O)
