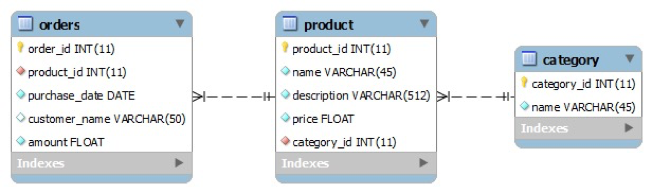
ORM Framework (Object Relational Mapping)
- Object Persistence 를 위한 프레임워크
- 객체와 테이블 사이에는 mismatch가 발생한다. 이를 위해 mapping시켜주는 프레임워크

DB에 데이터 persist를 위한 3가지 방법
1) JDBC
2) Spring JDBC
3) Hibernate (ORM Framework)
ORM libraries
1) DB의 데이터 구조와 자바의 객체 모델 간의 차이를 줄여준다. 2) 개발자는 객체 모델을 사용하여 프로그래밍을 하는데 집중 할 수 있다! 3) SQL문을 몰라도 객체 지향적으로 객체 모델에 기반해서 프로그래밍을 할 수 있다.
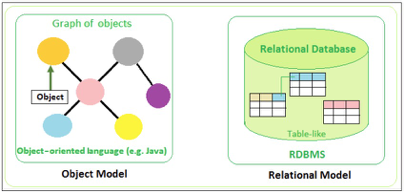
Object-Renational Mismatch
1) Granularity(세분성)
- 객체 지향 프로그래밍에선 학생 정보를 나타내고자 할 때 클래스에서는 Person클래스와 Address클래스 두 개가 요구 됨
- 데이터베이스에선 person테이블 하나만 존재하면 됨
2) Inheritance(상속)
- 객체 지향 프로그래밍에선 자연스러운 패러다임
- 데이터베이스에선 상속이란 개념이 존재하진 않음
3) Identity(식별성)
- 객체 지향 프로그래밍에선 2가지로 정의한다.
- 1) object identity(a==b): a와 b가 동일한 객체를 가리키는 경우
- 2) object equality(a.equals(b)): a와 b가 각각 가리키는 객체는 다르지만 해당 객체들 간의 필드 값들이 모두 같을 경우
- 데이터베이스 상에선 Key값이 같으면 같다고 볼 수 있다.
4) Association
- 객체 지향 프로그래밍에선 포인터와 같은 레퍼런스로 표현

- Department 객체에 대한 레퍼런스를 유지하고 있음
- 레퍼런스는 방향성이 존재함(양방향/단방향)
- 데이터베이스에선 외래키 컬럼을 사용해서 표현

- 외래키는 방향성이 존재하지 않는다.
5) Navigation
- 객체를 순회 할땐 다음과 같이 순회하게 됨
1
aUser.getBillingDetails().getAccountNumber()
- 데이터베이스에선 테이블들을 조인하여 특정 항목을 select하는 방식을 사용함
Association의 종류
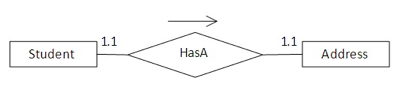
1) One-to-One

각각의 학생들은 단 하나의 주소를 가지기 때문에 1대1 관계를 유지 할 수 있음
Java에서 One-to-One Relationship

- 데이터베이스에서 One-to-One Relationship

2) One-to-Many
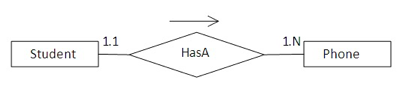
각각의 학생들은 여러 개의 전화 번호를 가질 수 있기 때문에 1:N 관계를 유지 할 수 있음
- Case1.
- 1) Java에서 One-to-Many Relationship
- 2) 데이터베이스에서 One-to-Many Relationship
- 1) Java에서 One-to-Many Relationship
- Case2.
- 1) Java에서 One-to-Many Relationship
- 2) 데이터베이스에서 One-to-Many Relationship
- 1) Java에서 One-to-Many Relationship
Hibernate의 개념
1) 강력한 고성능의 Java에서의 ORM 솔루션 2) Java클래스와 DB의 테이블사이에 매핑을 담당해준다.(자바의 데이터 타입과 SQL의 데이터 타입으로 부터) 3) 오픈 소스(LGPL)

Hibernate 라이브러리

Hibernate의 이점
1) ORM(Object-to-Relational Mapping) 매핑을 제공한다. 2) 저수준의 SQL문을 사용하여 JDBC코드의 양을 줄여준다.
Hibernate 3가지 구성
1) SessionFactory -> session을 만들어서 DB와 실제 커뮤니케이션
2) hibernate.cfg.xml -> 하이버네이트에 대한 설정파일
3) *.hbm.xml class mappings -> 객체와 테이블 사이에 대한 매핑 정보
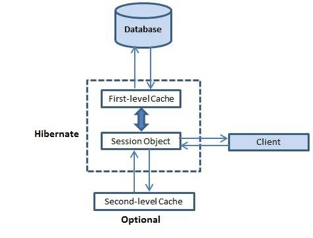
Hibernate를 사용한 애플리케이션의 아키텍처

1) 클라이언트가 유저 인터페이스를 통해 form데이터를 보내면 백엔드 영역에서 컨트롤러가 받아서 DAO계층을 이용하여 Data persistent를 유지한다. 2) DAO계층에서는 Hibernate API를 이용하여 Hibernate를 사용한다. 3) Hibernate는 JDBC API를 이용하여 JDBC를 사용한다. 4) JDBC를 통해 넘어오는 ResultSet이 넘어오고 Hibernate가 다시 객체로 변환하여 DAO계층으로 넘겨준다. 5) DAO계층은 다시 받은 것을 컨트롤러로 넘겨줘서 프론트 영역으로 넘겨준다.
Hibernate의 구성요소
1) SessionFactory: JDBC커넥션을 사용해서 DB를 접근하기 위해 내부적으로 SessionFactory로 Session을 생성 2) hibernate.cfg.xml: Hibernate와 관련된 설정파일 3) *.hbm.xml(class mappings): 객체와 테이블 사이에 매핑 정보를 설정
Hibernate의 동작원리
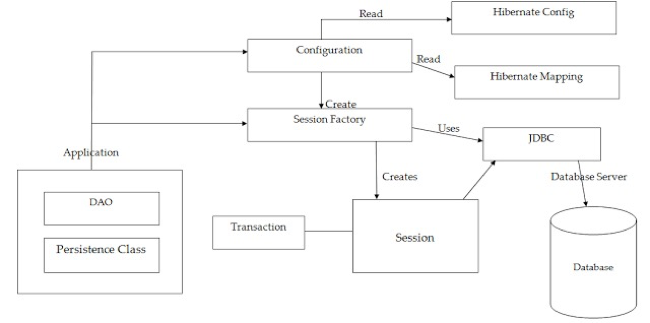
1) Configuration클래스를 사용해서 Hibernate와 관련된 설정 정보와 매핑정보를 읽어들인다. 2) Configuration클래스가 SessionFactory를 생성한다. 3) SessionFactory가 Session을 만들게 되어 JDBC를 사용해서 DB에 접근하게 된다. 4) 그 외에 트랜잭션과 관련된 클래스들이 존재하고 있다.
Hibernate의 아키텍처
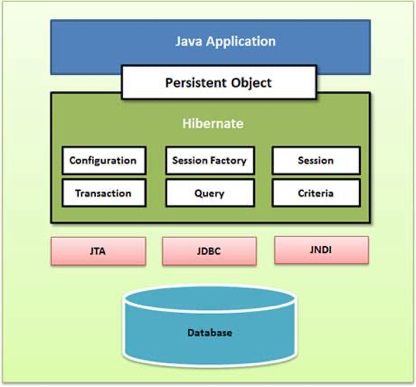 1) Configuration Object
1) Configuration Object
- 두 가지 정보를 담고 있음
- 1) Database 커넥션 정보(hibernate.cfg.xml)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <!-- JDBC Database connection settings --> <property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="connection.url"> jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testdb?useSSL=false&characterEncoding=UTF-8& serverTimezone=Asia/Seoul</property> <property name="connection.username">root</property> <property name="connection.password">csedbadmin</property> <!-- 우리가 사용하는 DB 정보입력--> <property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL8Dialect</property> <!-- hibernate가 콘솔에서 자동 생성하는 sql을 볼 것이냐 말것이냐 (true이면 생성하는 sql을 콘솔 창에서 볼 수 있음) --> <property name="show_sql">true</property> <!-- Table을 메뉴얼(수동)적으로 생성하는게 아니라 오토(자동)적으로 생성하게 한다 (create를 주면 애플리케이션 실행시 매번 테이블을 자동으로 생성하게 되어있음) --> <property name="hbm2ddl.auto">create</property> <!-- Mapping클래스 지정 --> <mapping class="testHibernate.Product" /> <mapping class="testHibernate.Category" /> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>- mapping class 예시
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
@Entity // DB테이블에 매핑되는 자바 클래스임을 표시 @Table(name="product") // 테이블명 설정, 디폴트는 테이블명이 클래스이름과 동일하게됨 public class Product { @Id // Primary Key @GeneratedValue // 자동으로 Key를 생성하라 @Column(name=“product_id”) // column이름 설정, 디폴트는 컬럼네임이 필드이름과 동일하게 됨 private int id; private String name; private int price; private String description; // Product가 Category를 가리키는 경우에 연관성을 지정해줄 필요가 있음 // 하나의 Category에는 여러 개의 Product가 존재 할 수 있으므로 Product입장에선 ManyToOne이 됨 // JoinColumn 어노테이션을 통해 컬럼명을 지정해 줄 수 있음 @ManyToOne(cascade=CascadeType.ALL) @JoinColumn(name="category_id") private Category category; }- 2) 객체와 테이블에 관련된 매핑 정보(*.hbm.xml)
2) SessionFactory Object
- session을 생성해냄
- 멀티 스레드 환경에서 안전한 객체이고 애플리케이션의 모든 스레드에 의해 사용 될 수 있음
- 단 한 번만 생성이 되고 계속 사용이 되게 되어있음
- SessionFactory.openSession()
- 실제 세션을 하나 만들고 다 사용한뒤 close후 flush하는 작업이 필요하다.
- 세션이 캐슁을 하고 있기에 캐쉬 내용을 flush해서 비워줘야 한다.
- Spring 프레임워크가 자동적으로 close를 시켜주므로 개발자는 close시켜줄 필요가 없다.
- SessionFactory.getCurrentSession()
- 실제 Session을 하나 얻어온다.
- open사용하지 않고 바로 호출해도 새로운 세션을 자동으로 만들어서 얻을 수 있다.
- Spring 프레임워크가 자동적으로 close를 시켜주므로 개발자는 close시켜줄 필요가 없다.
- 예시
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
public class PersonService {
// Spring 컨테이너에 보관하고 있는 sessionFactory bean을 의존성 주입
@Authowired
private SessionFactory sessionFactory;
public Person edit(Integer id, String firstName,
String lastName, Double money) {
// session 생성
Session s= sessionFactory.openSession();
// Transaction 시작
Transaction tx= s.beginTransaction();
// Session 얻어오기
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
// session의 get메소드에 인자로 매핑 할 클래스와 id(primary key)값을 주고 호출해서 DB로부터 해당 레코드를 읽어와 객체로 넘겨주게됨
Person person = (Person) session.get(Person.class, id);
person.setFirstName(firstName);
person.setLastName(lastName);
person.setMoney(money);
// 수정한 객체에 대한 upate
session.update(person);
// Transaction 커밋
tx.commit();
return person;
}
- 다음과 같이 Spring의 Transactional어노테이션을 활용하여 클래스 전체 메소드에 대해 트랜잭션 처리를 할 수도 있다.

3) Session Object
- entity개체에 대해서 CRUD연산을 수행하는 객체
- 애플리케이션과 데이터베이스를 연결해주는 역할
- 데이터베이스와 물리적 커넥션을 얻을 때 사용
- Thread-safe하지 않기 때문에 오랜 시간 동안 open된 상태로 두어선 안된다.

- Hibernate는 캐쉬가 존재 한다.
- Session객체와 데이터베이스 사이에는 캐쉬가 존재한다.
- 매번 바로 Session객체로부터 데이터베이스에 쓰는 것은 퍼포먼스에 영향을 줄 수 있기 때문에 캐쉬에 모아뒀다가 한 번에 작업을 처리한다.
Object states
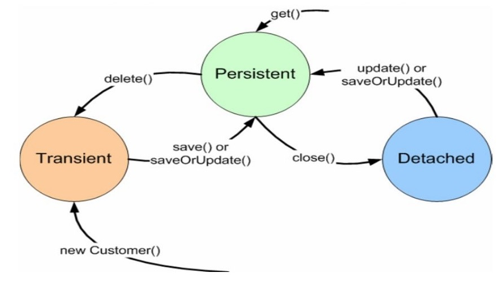
- 인스턴스를 맨 처음에 만들면 Transient상태가 된다.(메모리에 저장된 상태)
- save또는 saveOrUpdate메소드를 호출하면 Persistent상태로 바뀌게 된다.(DB에 저장된 상태, 하드디스크)
- Session을 close시키면 Detached상태가 되어 Session과 분리가 된다.
- 예제 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public class HibernateTest {
public static void main() {
Person person = new Person(); // Transient Object
person.setUserName("Test User");
SessonFactory sessionFactory =
new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
Sesson session = SessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction();
session.save(person); // Persistent Object
// persistent 상태에서 어떤 변경을 가하면 DB에 그대로 반영이 된다.
person.setUserName("Updated User");
person.setUserName("Updated User Again");
session.getTransaction().commit();
// setter메소드 호출 후 save하지 않았지만 결과는 "Updated User"가 나온다
session.close();
// Detached 객체이기 때문에 더 이상 hibernate가 변경상태를 추적하지 않는다.
person.setUserName("Updated User After session close");
}
}
Session Methods
1) get(Class clazz, Serializable id)
- 지정한 클래스에 매핑되는 테이블에서 id에 해당되는 레코드를 읽어서 객체가 넘어오게 됨
- 해당되는 id에 해당하는게 없으면 null값이 리턴 됨
2) save(Object object)
- object를 저장
- 리턴값으로는 저장된 entity의 id가 넘어오게 됨
- cascade 연산에 cascade=”save-update”하면 참조하는 객체까지 같이 저장됨
- 예를 들어, Student객체를 저장해도 참조하고 있는 Address객체도 함께 저장됨
2) saveOrUpdate()
- 기존에 이미 저장된게 있으면 update, 없으면 save
3) delete()
- persistent인스턴스를 데이터베이스에서 제거
- cascade 연산에 cascade=”delete”하면 참조하는 객체까지 같이 제거됨
- 예를 들어, Student객체를 제거해도 참조하고 있는 Address객체도 함께 제거됨
4) flush()
- Hibernate안에 캐쉬에 있는 내용을 데이터베이스에 반영(동기화)
- flush의 4가지 모드
- Always: 모든 쿼리를 수행할때마다 바로 캐쉬에 저장했다가 바로 flush(퍼포먼스엔 안 좋은 영향)
- Commit: 트랜잭션이 커밋될떄 flush
- Manual: 수동적으로 flush메소드를 호출해서 사용
- Auto: 디폴트 모드, 트랜잭션이 커밋 또는 쿼리가 실행되기 전에 시스템에서 알아서 flush
- hibernate.cfg.xml 설정 파일에서 다음과 같이 모드 설정 가능
1
<property name="org.hibernate.flushMode" value="COMMIT"/>
예를 들어, 다음과 같은 작업을 수행한다고 가정 했을 때
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Step 1: Begin transaction Step 2: Create employee A Step 3: Create employee B Step 4: Associate A with its manager C Step 5: Look up all employees reporting to C Step 6: Associate B with its manager D Step 7: Look up all employees reporting to D Step 8: Commit transaction
- A,B,C,D는 디비가 아닌 캐쉬에 저장되어있는 상태있기기에.스텝5,7 수행시 디비에 아무것도 없기에 결과가 제대로 나오지 않음
- 따라서 적절한 타이밍에 flush시켜줘야함
5) close()
- Session을 닫음
- Spring에서는 알아서 close를 시켜주기에 호출 할 필요가 없다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
@Repository
@Transactional
public class ProductDaoImpl implements ProductDao {
@Autowired
private SessionFactory sessionFactory;
public Product getProductById (int id) {
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
Product product = (Product) session.get(Product.class, id);
return product;
}
public void addProduct (Product product) {
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
session.saveOrUpdate(product);
session.flush();
}
}
6) Query createQuery(String queryString)
- Query 객체를 생성하여 좀 더 디테일하게 쿼리를 만들 때 사용
- HQL(Hibernate Query Language)을 사용
- 예제 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public List<Product> getProductList() {
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
Query<Product> theQuery =
session.createQuery("from Product“, Product.class);
List<Product> products = theQuery.getResultList();
return products;
}
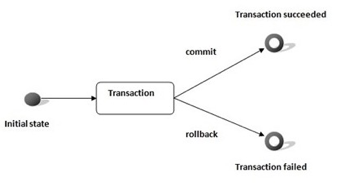
4) Transaction Object
- 데이터베이스와 관련된 작업의 단위를 나타냄

5) Query Object
- session.createQuery()메소드를 생성
- SQL 또는 HQL을 사용할 수 있음
- parameter를 지정하거나 조회 되는 result의 개수를 지정 할 때 주로 사용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public List<Product> getProductList() {
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
Query<Product> query =
session.createQuery("from Product order by name“, Product.class);
List<Product> products = query.getResultList();
return products;
}
HQL
- SQL과 유사함
- 테이블이나 컬럼 이름을 사용하는게 아니라 클래스나 속성이름을 사용
- 키워드는 대소문자 구분하지 않음
- 자바 클래스나 속성이름은 대소문자를 구분함
- 실행 방법
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
1. hql 작성
String hql= "Your Query Goes Here";
2. session으로 부터 쿼리 객체 생성
Query query = session.createQuery(hql);
3. 레코드들을 리스트 형태로 조회하는 쿼리 실행
List listResult = query.getResultList();
3-2. update 쿼리 실행
int rowsAffected = query.executeUpdate();
- 예시

1) 복수 레코드 리스트 조회 쿼리
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
String hql = "from Category";
Query<Category> query = session.createQuery(hql, Category.class); // 두 번째 인자로 실제로 조회하는 클래스 이름을 명시
List<Category> listCategories = query.getResultList();
for (Category aCategory : listCategories) {
System.out.println(aCategory.getName());
}
2) 단일 레코드 조회 쿼리
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
String hql = "from Product where category.name = 'Computer'"; // 내부적으로는 hibernate에 의해서 JOIN연산이 이뤄져서 처리가 된다.
Query<Product> query = session.createQuery(hql, Product.class);
List<Product> listProducts = query.getResultList();
for (Product aProduct : listProducts) {
System.out.println(aProduct.getName());
}
3) 업데이트 쿼리
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
String hql = "update Product set price = :price where id = :id"; //placeholder가 들어가 있음 (:placeholder이름)
// Update/Delete queries can not be typed.
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") // warning을 나오지 않게 하기 위한 anno
Query query = session.createQuery(hql); // 클래스 타입을 명시 안해주면 waring 발생
query.setParameter("price", 488.0); // 해당 되는 placeholder에 값 세팅
query.setParameter("id", 43); // 해당 되는 placeholder에 값 세팅
int rowsAffected = query.executeUpdate();
if (rowsAffected > 0) {
System.out.println("Updated " + rowsAffected + " rows.");
}
4) 삭제 쿼리
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
String hql = "delete from OldCategory where id = :catId";
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
Query query = session.createQuery(hql);
query.setParameter("catId", 1);
int rowsAffected = query.executeUpdate();
if (rowsAffected > 0) {
System.out.println("Deleted " + rowsAffected + " rows.");
}