우선순위 큐(Priority Queue)란?
- 우선순위에 따라 우선순위가 높은 객체가 먼저 나오는 자료구조
- 우선순위 큐는 3가지 방법으로 구현할 수 있다.
- 1)배열 사용
- 데이터 삽입, 삭제과정에서 데이터를 밀고 당기는 연산을 해야 하는 단점이 존재
- 2)연결리스트 사용
- 연결리스트로 우선순위 큐를 구현하였을 경우 삽입의 위치를 찾기 위해 첫 번째 노드부터 마지막에 저장된 노드까지 순회해야 하는 단점
- 3)Heap을 사용
- 가장 일반적인 사용 방법!
- 1)배열 사용
Heap
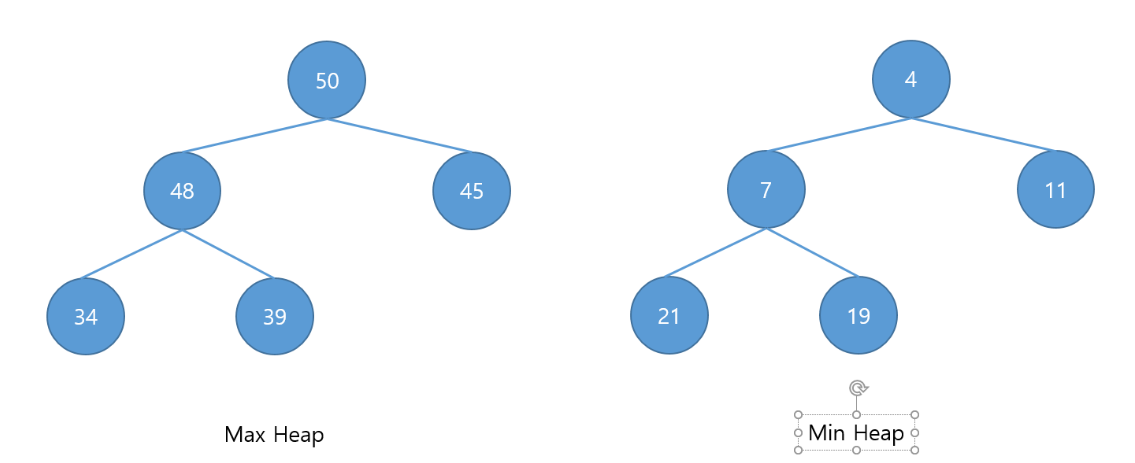
- 우선순위에 따라 우선순위가 높은 객체가 먼저 나오는 트리 구조의 큐
- 부모의 노드는 항상 자식의 노드보다 클 경우를 Max heap, 작을 경우를 Min Heap
- Heap의 삽입/삭제 과정
Java에서의 우선순위 큐 구현
- java.util.PriorityQueue를 사용
- java.util.PriorityQueue의 경우 기본 Heap구성은 minHeap(우선 순위가 낮은 것부터)으로 구성된다.(디폴트)
- 만약 우선순위가 maxHeap(우선 순위가 높은 것부터)으로 구성하기 위해서 Collections.reverseOrder()를 인자로 추가
1
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
Java에서 우선순위 큐 구현시 객체의 우선순위를 나타내는 방법
- 1) 기본 타입
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
//int형 priorityQueue 선언 (우선순위가 낮은 숫자 순)
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
//int형 priorityQueue 선언 (우선순위가 높은 숫자 순)
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
//String형 priorityQueue 선언 (우선순위가 낮은 문자 순)
PriorityQueue<String> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
//String형 priorityQueue 선언 (우선순위가 높은 문자 순)
PriorityQueue<String> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
// 출처: https://coding-factory.tistory.com/603
- 2) 큐에 저장될 객체(Student)에 Comparable인터페이스의 compareTo 메서드를 구현하는 방법
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
// Comparable 구현
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
private String name;
private int score;
public Student(String name, int score) {
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student input) {
int result = Integer.compare(score, input.score);
if( result == 0 ) {
result = input.name.compareTo(name);
}
return result;
} // 시험 점수가 높은 사람을 top으로 위치시키고 동점자의 경우 이름의 사전순으로 정렬
@Override
public String toString() {
return "이름 : " + name + " 점수 : " + score;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// main
PriorityQueue<Student> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.reverseOrder());
priorityQueue.add(new Student("김석진", 100));
priorityQueue.add(new Student("박석진", 90));
priorityQueue.add(new Student("진석진", 95));
priorityQueue.add(new Student("구석진", 88));
priorityQueue.add(new Student("다석진", 100));
priorityQueue.add(new Student("사석진", 100));
priorityQueue.add(new Student("나석진", 100));
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// 출력
이름 : 김석진 점수 : 100
이름 : 나석진 점수 : 100
이름 : 다석진 점수 : 100
이름 : 사석진 점수 : 100
이름 : 진석진 점수 : 95
이름 : 박석진 점수 : 90
이름 : 구석진 점수 : 88
- 3) PriorityQueue생성 시 생성자로 Comparator인터페이스를 구현한 객체(익명 함수 compare메서드 구현)를 넘기는 방법
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
// comparator 이용
public class Student {
private String name;
private int score;
public Student(String name, int score) {
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "이름 : " + name + " 점수 : " + score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
// main
PriorityQueue<Student> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student first, Student second) {
int result = Integer.compare(second.getScore(), first.getScore());
if( result == 0 ) {
result = first.getName().compareTo(second.getName());
}
return result;
}
}) ;
priorityQueue.add(new Student("김석진", 100));
priorityQueue.add(new Student("박석진", 90));
priorityQueue.add(new Student("진석진", 95));
priorityQueue.add(new Student("구석진", 88));
priorityQueue.add(new Student("다석진", 100));
priorityQueue.add(new Student("사석진", 100));
priorityQueue.add(new Student("나석진", 100));
while( !priorityQueue.isEmpty() ) {
Student student = priorityQueue.poll();
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// 출력
이름 : 김석진 점수 : 100
이름 : 나석진 점수 : 100
이름 : 다석진 점수 : 100
이름 : 사석진 점수 : 100
이름 : 진석진 점수 : 95
이름 : 박석진 점수 : 90
이름 : 구석진 점수 : 88
